Cloud services from the biggest names like Amazon, Microsoft, Google, IBM, and Alibaba continue to compete for consumer business in 2018 because it brings ease of use, security, increased productivity, and apps integration where there is Internet without using storage devices.
 It’s a revolutionary way to deliver computing power to end users: simply put, extremely large data centers are made available through fast but low-cost connectivity. How important is it? Perhaps, extremely indispensable. Even the giant company Microsoft spent 90% of its R&D budget as early as 2011 in cloud computing research!
It’s a revolutionary way to deliver computing power to end users: simply put, extremely large data centers are made available through fast but low-cost connectivity. How important is it? Perhaps, extremely indispensable. Even the giant company Microsoft spent 90% of its R&D budget as early as 2011 in cloud computing research!
Embedded from uCollect Infographics
Users produce, amass, share, and store huge volumes of personal and work data and the cloud makes it possible to access data anytime and anywhere economically. In fact, Cloud Management allows individuals and IT teams to use computing suites in free, subscription or pay-as-you-go modes. It enables consistent management of back-end and front-end in real time 24/7 while enabling users to trim-down costs and backup data efficiently. It is ubiquitous in the workplace, at home, and even at play.
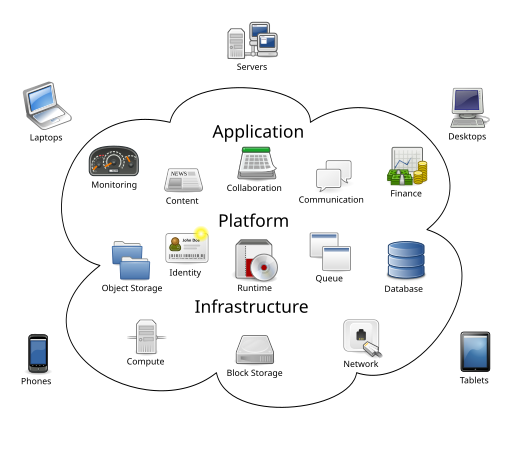
Kinds of Cloud Computing
- Software-as-a-Service (SaaS)
- Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS)
- Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS)
Software-as-a-Service
This is the top-revenue earner of all Cloud services and easily generates more than half of the cloud’s total revenue. Basically, a third party provider hosts applications and makes them available to customers over the Internet. If you’ve ever used Google Docs, Microsoft 365, Adobe or Salesforce, then you have a clear idea about how SaaS works. It is popular in customer service, HR solutions, and productivity applications. In effect, instead of downloading an expensive software and maintaining a large data center (or a least a huge hard drive on your local PCs), you can run the software without problems of installing and updating, while remaining collaborative and on-point. The terms are flexible and scalable with businesses able to integrate their own software into SaaS.
For businesses, the benefits of cloud computing are cost savings and improved business agility and responsiveness. – Statista
To date, the cloud is a 3-way battle between the pioneer Amazon Web Services which was started in 2006 (40% globally), Microsoft Azure (11%), and Google Cloud Platform (8%). It generates billions of dollars globally, with the public cloud earning $130B in 2017. Depending on the needs and security requirements, customers can choose between public, private, and hybrid. The choice is made based on several parameters and ultimately should be on how your cloud infrastructure aligns with your business strategy.
In short, it makes life easier for companies and end-users on the go – communicating across different locations and timezone. SaaS is vendor-controlled and accessible to multiple users through browsers or light application.You can also be on multiple clouds as being on one doesn’t exclude you from being on others; which can be confusing and time-consuming when you need to integrate data on the fly. There are merits to using multiple clouds because companies can avoid vendor lock-ins, enjoy more robust storage, and take advantage of specific strengths of each cloud service. On the other hand, embracing a single cloud platform ensures that all your apps “talk” to each other as they are being run from one system, ensure accurate real-time analytics or reporting, unified recording of customers, simple interface, and single log-in.
Platform-as-a-Service
In the past, enterprise concentrated on SaaS and IaaS. However, PaaS has gathered momentum with the most prominent AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Azure, Appfog, Engine Yard, Google App Engine, Bluemix, Cloud Foundry, OpenShift, Heroku, Stackato, Apprenda, and Matrix. In this set-up, the vendor provides the user both the hardware and software tools needed to create, manage, and deploy its applications. The process is simple compared to IaaS because selecting, buying, and configuring both the software and hardware is reduced.
Infrastructure-as-a-Service
The Infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS) market was worth a total of $25 billion a couple of years ago and is projected to reach $45 billion by 2018. In this model, a third party provider such as Amazon, Microsoft, Google, IBM, Oracle and AliCloud hosts and maintains infrastructure, software and the like on behalf of the customer so that the company does not need to worry about scalability – it remains stable whether more people use the website or the app.
Things to Consider When Choosing the Cloud Service
Nasuni has been running benchmark tests among the three Cloud providers. The latest done in 2015 shows Microsoft leading for two straight years, followed by Amazon, and trailed by Google in third place. Undoubtedly, much has changed and more competitors such as IBM, HP, Rackspace, and Alicloud have joined field but the parameters have hardly changed. Cloud choice is based on:
- Performance
- Stability
- Cost
- Scalability
- Support/Maintenance
- Global Reach or Availability
- Errors and
- Monitoring

The downside to using cloud services would be a slow or unstable Internet, making on-demand access to shared services impossible. This a major factor when companies choose countries to outsource to. In a manner of speaking, Internet speed becomes the bottleneck to cloud productivity, especially in the face of global teams beating the clock on impending deadlines.
Attribution Short Facts: By RTCS (Own work) [CC BY-SA 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)], via Wikimedia Commons
Attribution Cloud computing diagram: By Sam Johnston [CC BY-SA 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)], via Wikimedia Commons


















